Triggers are database operations which are automatically performed when an action such as Insert, Update or Delete is performed on a Table or a View in database.
Triggers are associated with the Table or View directly i.e. each table has its own Triggers.
There are two types of Triggers.
1) After Triggers : These triggers are executed after an action such as Insert, Update or Delete is performed.
2) Instead of Triggers : These triggers are executed instead of any of the Insert, Update or Delete operations.
For example, let’s say you write an Instead of Trigger for Delete operation, then whenever a Delete is performed the Trigger will be executed first and if the Trigger deletes record then only the record will be deleted.
Let us discuss these two type of Triggers by example.
Here are some After Triggers examples :
Scenario 1 : Insert Triggers
Below is an example of an After Insert Trigger. Whenever a row is inserted in the Student Table, the following trigger will be executed. The newly inserted record is available in the INSERTED table. The following Trigger is fetching the StudentId of the inserted record and the fetched value is inserted in the StudentLog table.
Triggers are associated with the Table or View directly i.e. each table has its own Triggers.
There are two types of Triggers.
1) After Triggers : These triggers are executed after an action such as Insert, Update or Delete is performed.
2) Instead of Triggers : These triggers are executed instead of any of the Insert, Update or Delete operations.
For example, let’s say you write an Instead of Trigger for Delete operation, then whenever a Delete is performed the Trigger will be executed first and if the Trigger deletes record then only the record will be deleted.
Let us discuss these two type of Triggers by example.
Here are some After Triggers examples :
Scenario 1 : Insert Triggers
Below is an example of an After Insert Trigger. Whenever a row is inserted in the Student Table, the following trigger will be executed. The newly inserted record is available in the INSERTED table. The following Trigger is fetching the StudentId of the inserted record and the fetched value is inserted in the StudentLog table.
Scenario 2 : Update Trigger
Below is an example of an After Update Trigger. Whenever a row is updated in the Student Table, the following trigger will be executed. The updated record is available in the INSERTED table. The following Trigger is fetching the StudentId of the updated record. In order to find which column is updated, you will need to use UPDATE function and pass the Column name of the Table to it. The UPDATE function will return TRUE for a Column if its value was updated else it will return false.Finally based on which column of the record has been updated a record (containing the CustomerId and the appropriate action) is inserted in the StudentLog table.
Now let us update two columns of the table and see the result set. That will insert 2 rows (row number 3 & 4) in log table with the entry of updated column names as below :
Now let us update one column of the table and see the result set. That will insert 1 rows (row number 5) in log table with the entry of updated column name as below :
Scenario 3 : Delete Trigger
Below is an example of an After Delete Trigger. Whenever a row is deleted in the Student Table, the following trigger will be executed. The deleted record is available in the DELETED table. The following Trigger is fetching the StudentId of the deleted record and the fetched value is inserted in the StudentLog table.
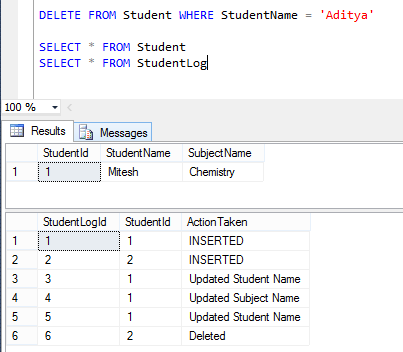
Now let us Delete one row of the table and see the result set. That will insert 1 rows (row number 6) in log table with the entry of deleted column Id as below :
Instead Of Triggers :
Below is an example of an Instead Of Delete Trigger. Whenever anyone tries to delete a row from the Student table the following trigger is executed. Inside the Trigger, I have added a condition that if record has StudentId value 1 then such a record must not be deleted and an error must be raised. Also a record is inserted in the StudentLog table.
If the StudentId value is not 1 then a delete query is executed which deletes the record permanently and a record is inserted in the StudentLog table.
Now, when we try to delete StudentId 1, we'll get below error message :
While, when we try to delete other than StudentId 1 data, it gets successfully deleted :
DROP TABLE Student
DROP TABLE StudentLog
Thank you for reading!!!!